Diols Diols (MPD & ND)
Features
MPD
Softness
Kuraray Polyol inhibits cohesion. This allows for increased operating efficiency.
Hydrolysis resistance
Hydrolysis resistance is good; MPD can inhibit the hydrolysis resistance of polyurethanes.
ND
Appropriate crystallinity
By moderately disrupting orientation (crystallinity), it imparts strength and flexibility to polyurethane.

Left:MPD at room temp.
Right:ND heating at 60°C
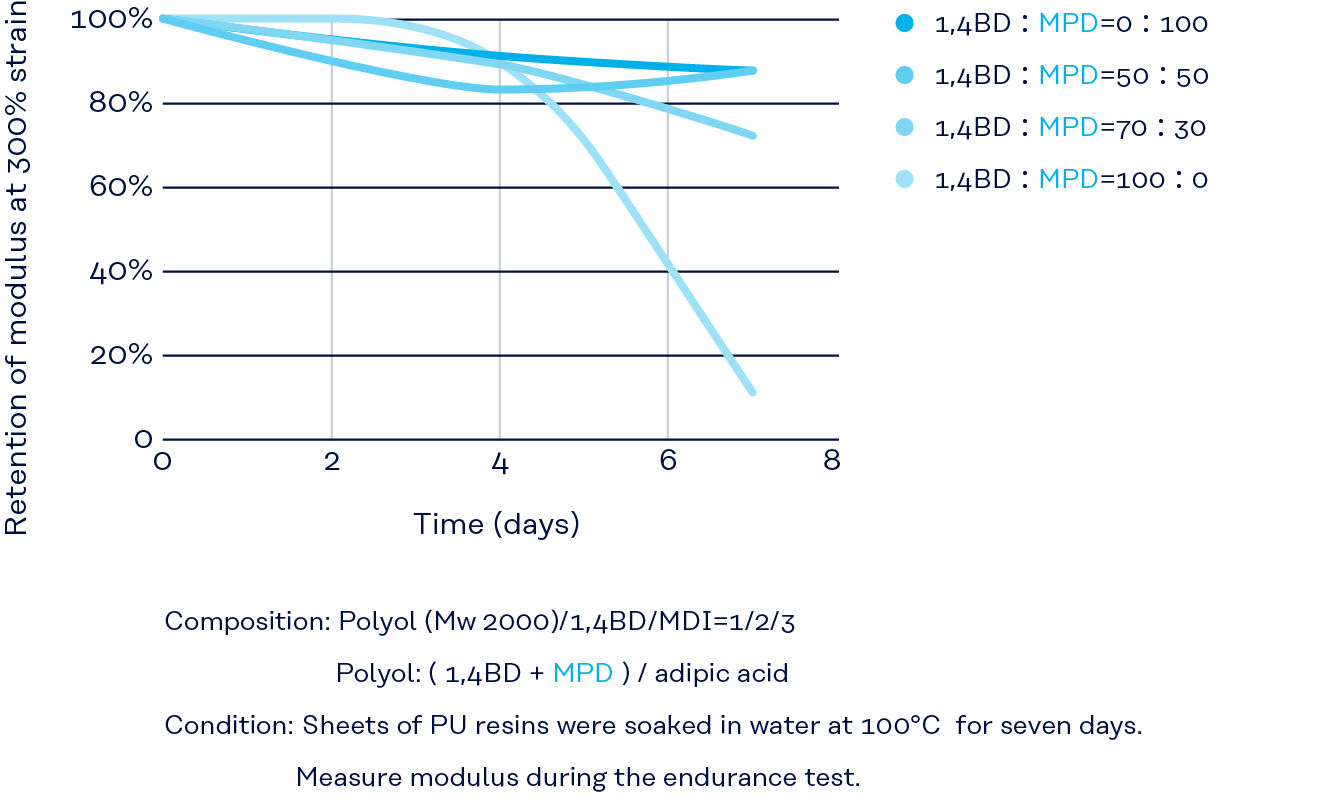
Hydrolysis resistance (MPD)
The hydrolysis resistance of PU resin from MPD-based polyester polyol is high even MPD portion is small as an ingredient of polyester polyol.
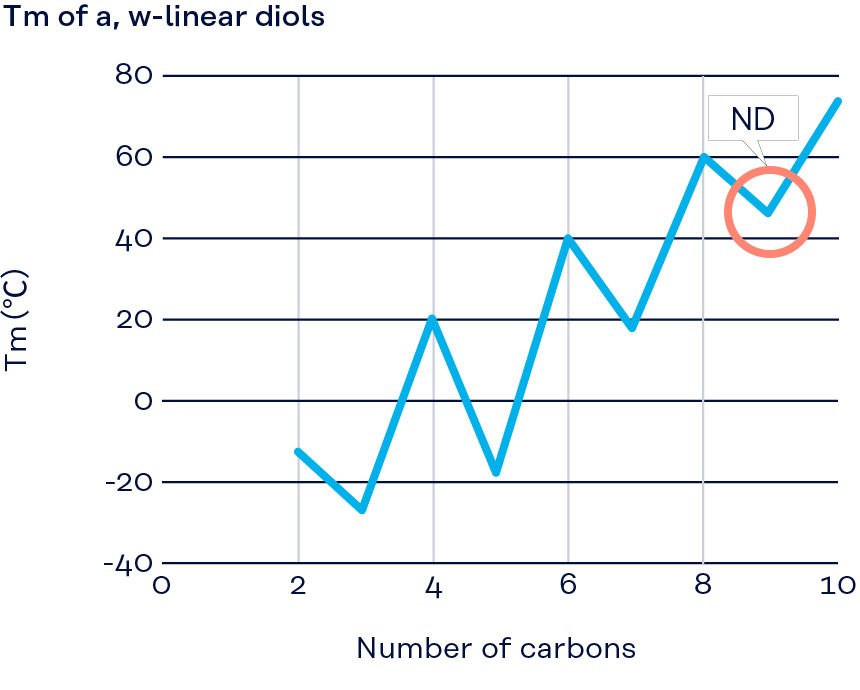
Appropriate crystallinity (ND)
Compared to diols with even carbon numbers, molecular chains are less likely to be oriented, and crystallinity is appropriately suppressed, resulting in a lower melting point. The moderate crystallinity gives the resin strength and flexibility and improves transparency.
Applications
MPD
- Polyurethanes (polyols, chain extenders)
- Solvents
- Acrylate Monomer
ND
- Polyurethanes (polyols, chain extenders)
- Polyester
- UV monomer, oligomer
- Acrylate Monomer




